Google Cloud Storage
Bucket Name
Your Google Cloud administrator must create and configure a storage bucket that will be used to store your organizations recording data.
Storage buckets
Google Cloud Storage uses buckets to organize and control access to your data. Everything that you store in Cloud Storage must be contained in a bucket. More information on buckets can be found here.
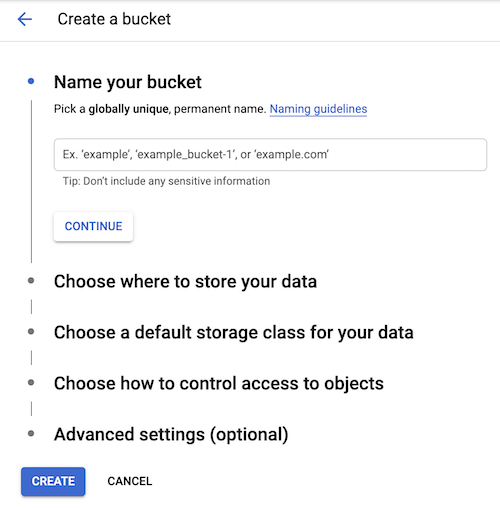
Creating a bucket
Your Cloud Storage administrator must create and configure a storage bucket.
The image below depicts the steps to create a bucket using the Google Cloud console.
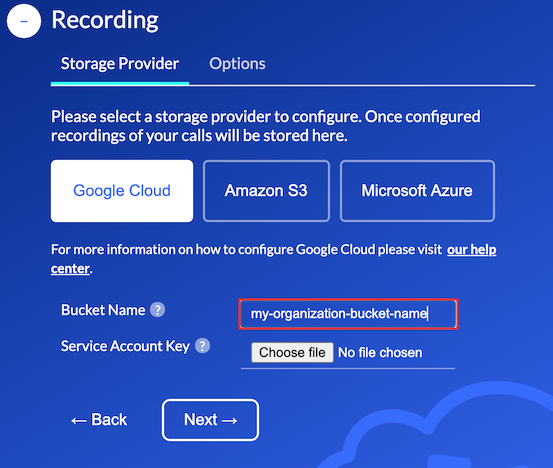
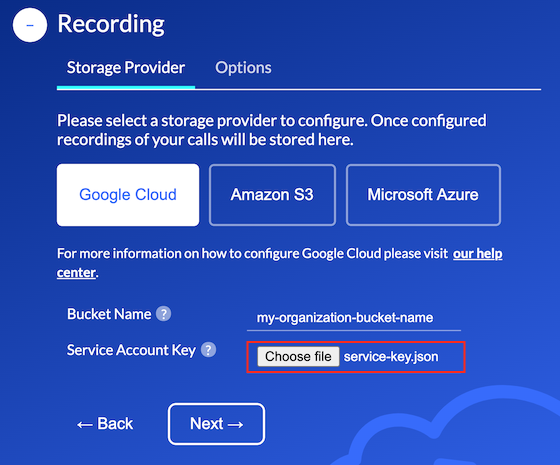
Once your bucket has been successfully created and configured the name of this bucket must be entered in
the Bucket Name property under the Auvious Storage Provider configuration page, as depicted below.
Service Account Key
A Service Account Key allows Auvious to securely access your organizations storage service directly. Generate the key as JSON, then base64-encode the entire JSON file and paste that base64 string into the Auvious Service Account Key field.
Service Account
To create a Service Account Key your Google Cloud administrator will first have to create and configure a valid Service Account. A service account is a special kind of account used by applications to make authorized API calls.
Troubleshooting
| Error/message | Likely cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| 401/403 storage.objects.* denied | Service account missing Storage Object Admin/Writer/Viewer on bucket | Grant required IAM roles to the service account used in storageProviderKey; redeploy key if rotated |
| 404 No such bucket | Bucket name wrong or service account lacks storage.buckets.get | Correct storageProviderBucket; ensure account has bucket-level access |
| 301 Moved Permanently | Bucket in different location than expected | Confirm bucket location and keep using that region (GCS is multi-regional; no region override) |
| 429 / 5xx with retries | API throttling or transient errors | Retry or raise throughput thresholds; avoid bursty verification runs |
| invalid base64 / credential parse failure | storageProviderKey not valid base64 service account JSON | Re-encode the service account JSON to base64 and re-enter |
The image below depicts the steps to create a Service Account and Service Account Key respectively.
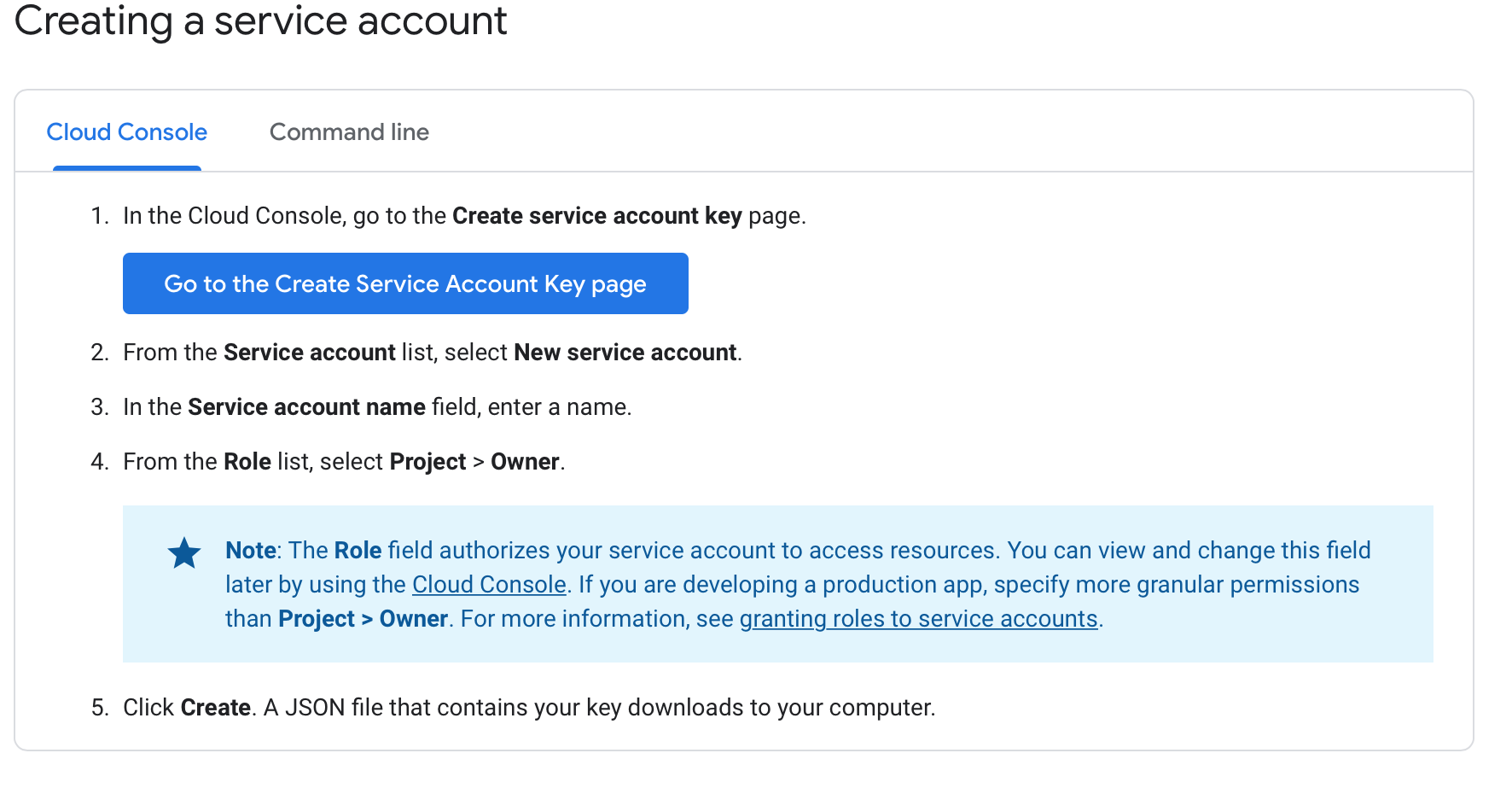
For detailed information on creating a service account see here.
Create Service Account Key
Once you have successfully created a Service Account you will need to generate a Service Account Key. Create a key of type JSON as depicted below.
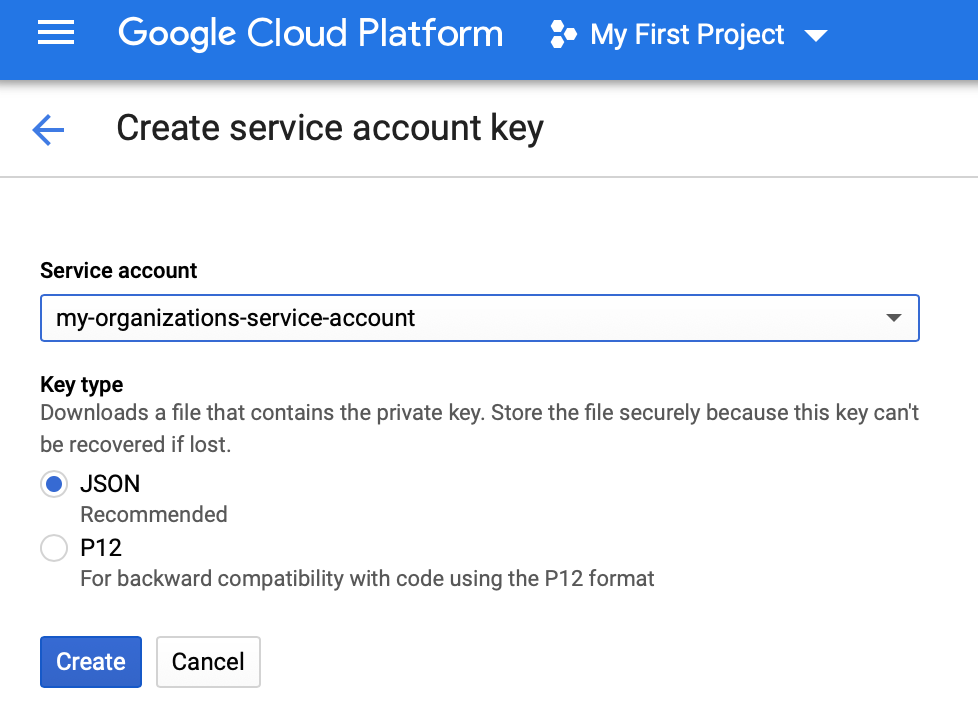
Once you create your key it will be downloaded locally as a JSON file. Base64-encode the file contents (for example,
cat key.json | base64) and paste that string into the Service Account Key field under the Auvious Storage Provider
configuration page, as depicted below.
Permissions
The following permissions need to be assigned for correct access:
- storage.buckets.get
- storage.objects.get
- storage.objects.create
- storage.objects.delete
- storage.objects.list (recommended for verification flows)
- storage.objects.signUrl
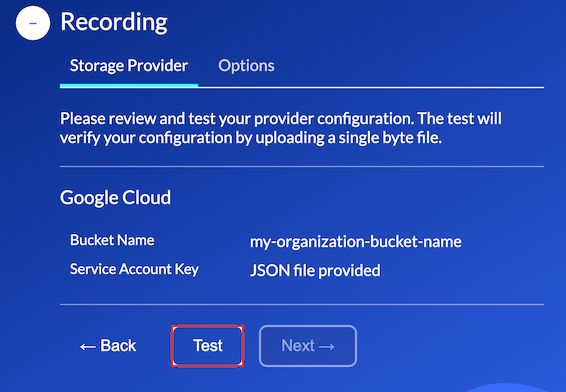
Review & Test
In the final step you can review and go back to make any necessary corrections.
When you are ready, you can test your configuration. Verification performs bucket lookup plus object upload, download, copy, delete, and a signed URL check, so the permissions above (and signing ability of the service account) must be present. Tight quotas can surface as 429/5xx during the test—retry after reducing burstiness or raising limits.